|
The genetic basis of chromosomally mediated penicillin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Ngo):
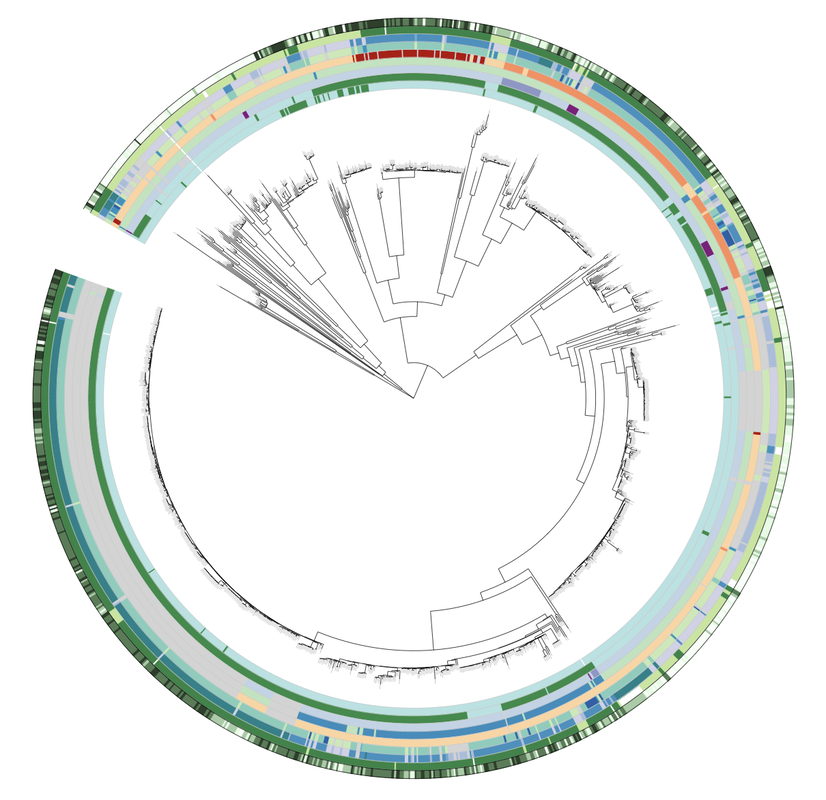
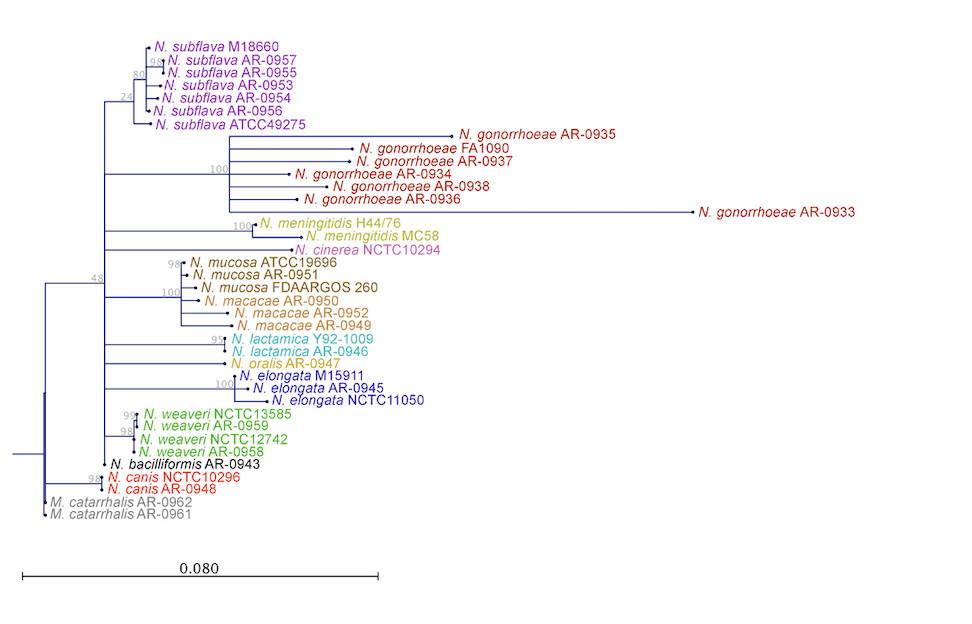
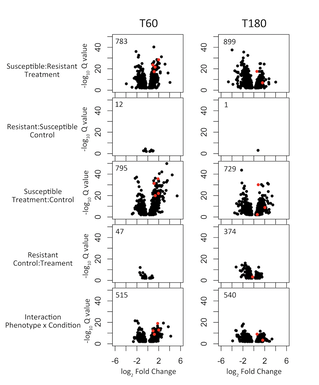
Chromosomally mediated penicillin resistant Ngo strains (CMRNG) have multiple genetic mutations that contribute to reduced susceptibility, however the complete genetic basis has yet to be deciphered. In collaboration with Robert Nicholas at University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, we are using a combination of population genomics and transformations to try to illuminate the unknown mutations (Factor X) that underlie this phenotype. Characterizing the Neisseria resistome across commensals and pathogens: Ngo has been repeatedly demonstrated to acquire resistance from close commensal relatives within the genus, however the resistance genotypes and subsequent phenotypes in these other species are infrequently described. In this ongoing work we attempt to profile the genetic mechanisms available for transfer from commensals to pathogen. Development of point of care resistance diagnostics using RNA signatures: With the dramatically increasing incidence of antimicrobial resistance, diagnostics that rapidly inform on susceptibility are urgently needed to improve the time to appropriate therapy. Quantitative assessment of antibiotic-responsive RNA transcripts is a promising phenotype-based diagnostic approach, as it can distinguish resistant and susceptible strains within minutes to hours. Here, we illuminate signatures of susceptibility for Ngo. |